Tag: International law
-
Release of a cold-blooded killer illustrates the racism of Israeli society
23rd April 2016 | International Solidarity Movement, al-Khalil team | Hebron, occupied Palestine Yesterday, Elor Azraya, a soldier in the Israeli army, infamous for the extrajudicial execution of Abed al-Fattah al-Sharif in occupied al-Khalil (Hebron), has been released to celebrate the Jewish holiday of Pessach with his family. 21-year old Abed al-Fattah al-Sharif was lying…
-
Palestinian youth intentionally run over in Hebron
22st April 2016 | International Solidarity Movement, al-Khalil team | Hebron, occupied Palestine On the afternoon of 21st April 2016, an Israeli settler ran down a Palestinian youth with his car, causing critical injuries, near the Ibrahimi mosque in occupied al-Khalil (Hebron). Two settlers were driving down the road connecting Shuhada Street and Kiryat Arba in…
-
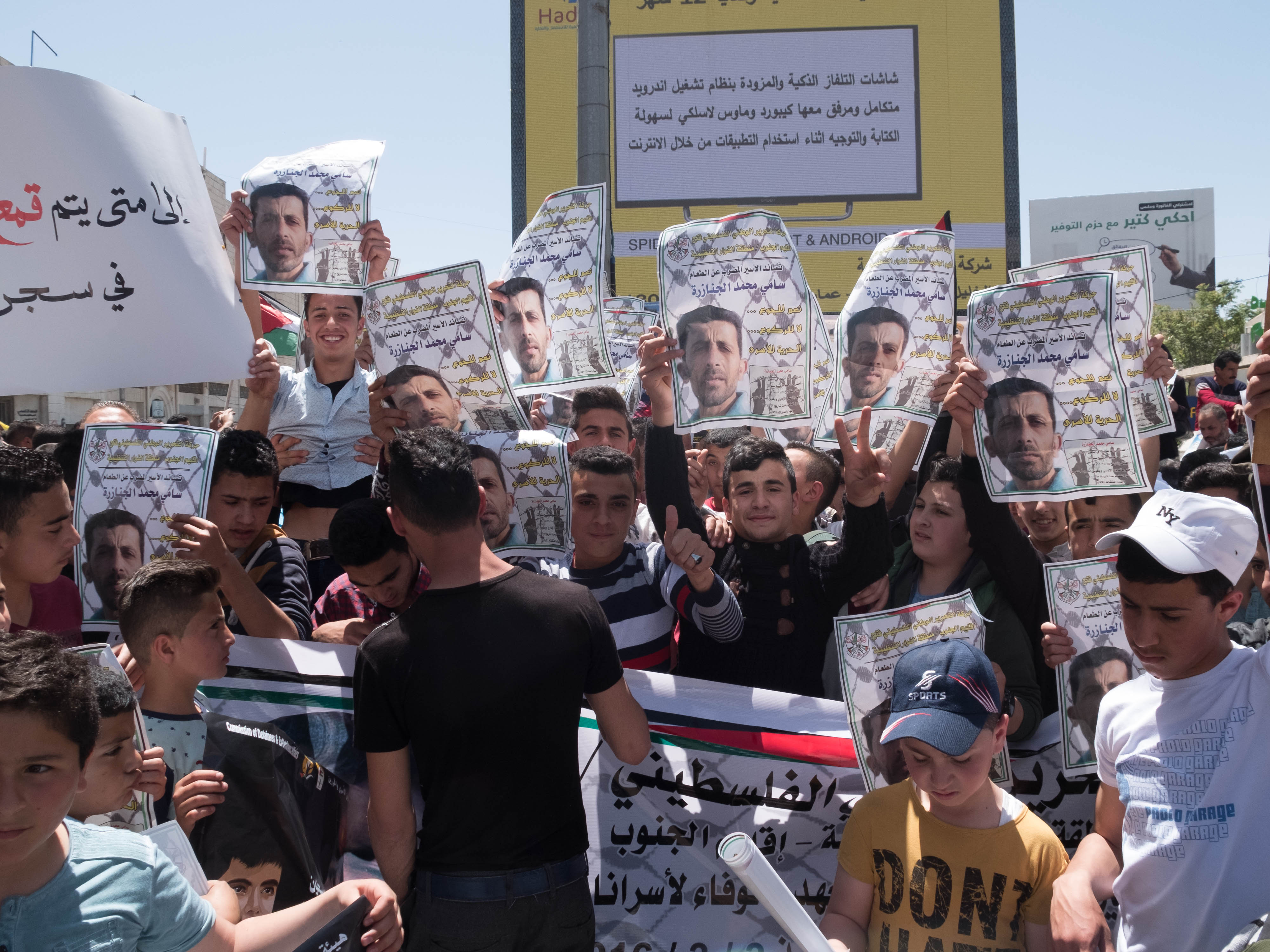
Sami Janazreh enters 46th day of hunger strike
17th April 2016 | International Solidarity Movement, Al-Khalil Team | Hebron, occupied Palestine Today volunteers from ISM attended a demonstration in Al-Khalil for Prisoners’ Day. Once the main demonstration had ended in the city a group of young Palestinians invited the volunteers to the Fawwar refugee camp outside the city. At the camp they were…