Author: ISM Media
-
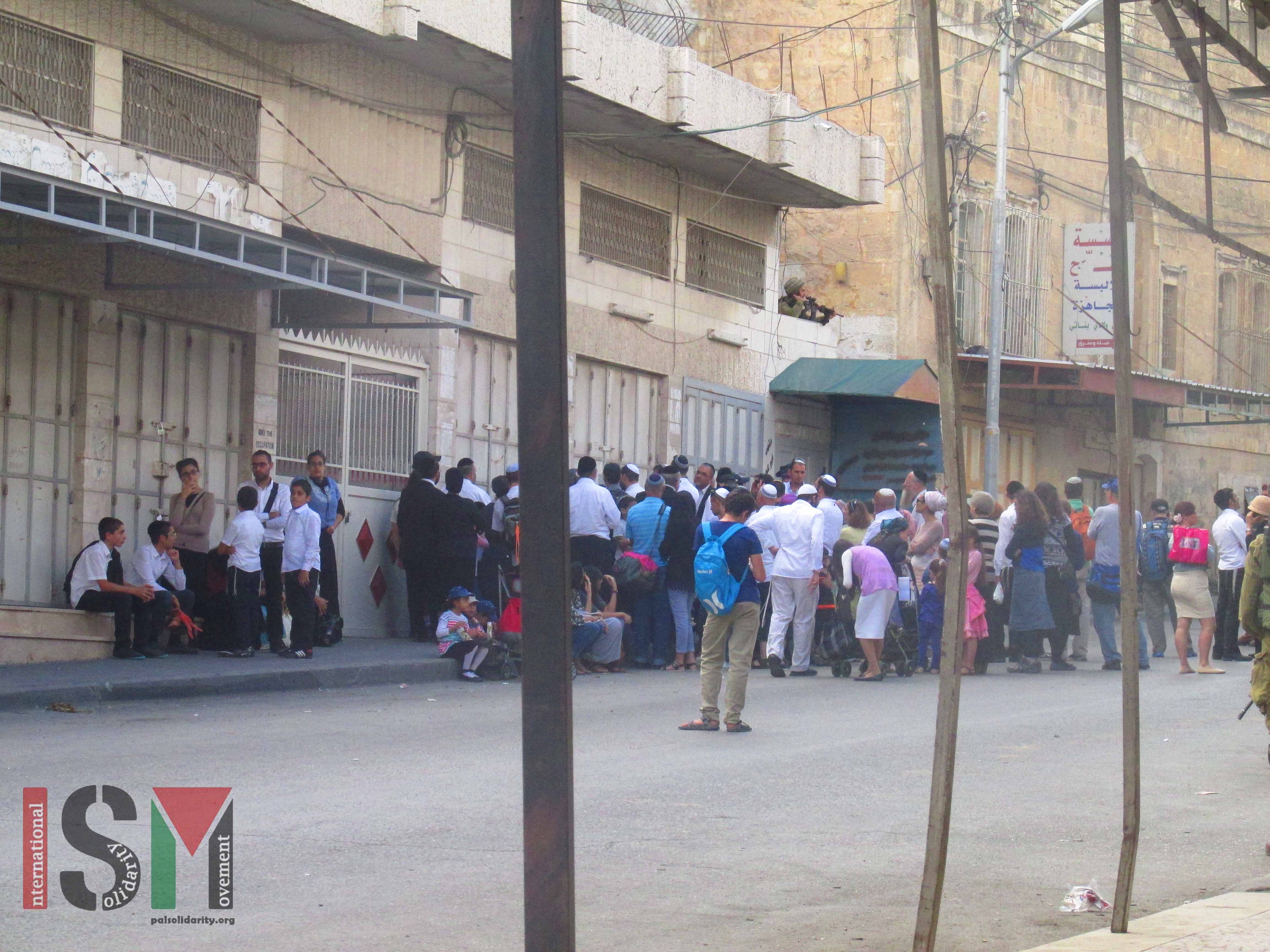
Jewish holiday leads to large influx of settlers, zionist tourists, and Israeli soldiers
12th October 2014 | International Solidarity Movement, Khalil team | Hebron, Occupied Palestine Today in al-Khalil (Hebron), as part of the Jewish holiday of Sukkot, thousands of settlers and Zionist tourists descended upon the city. The Israeli military presence in Hebron, which is already a large an oppressive part of everyday life, greatly increased. Hebron is the…
-
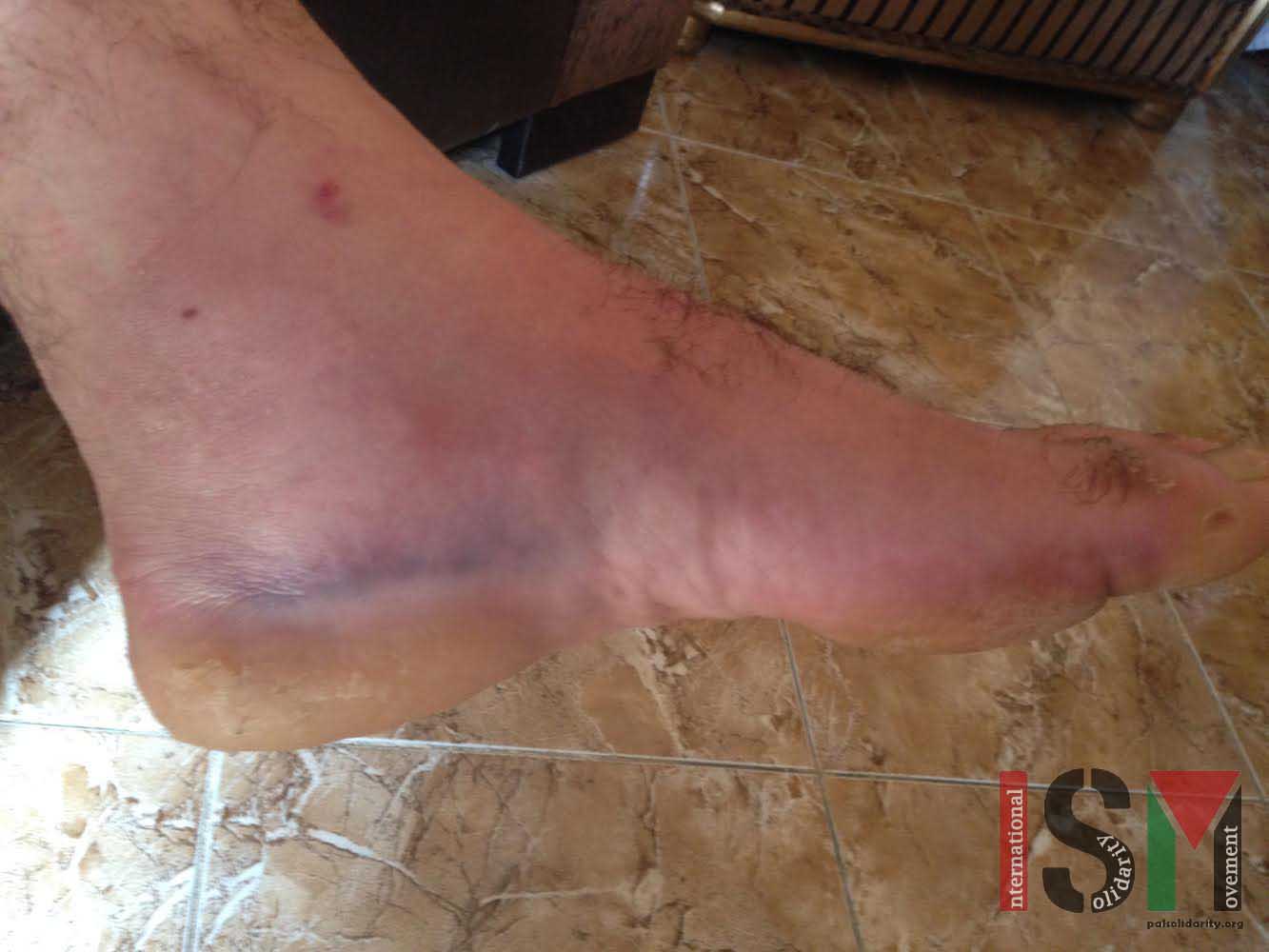
Israeli forces arrest disabled Palestinian man
9th October 2014 | International Solidarity Movement, Khalil team | Hebron, Occupied Palestine Yesterday at approximately 10 PM in the Qeitun region of Al-Khalil (Hebron), a group of 6 Israeli soldiers accused 14-year-old Amjad Taha of throwing fire crackers at them outside of his home. Amjad’s cousin, Muhammad Taha (17 years-old), was standing close by with his 2-year-old…
-
Palestinian family attacked by settlers while harvesting olives
10th October 2014 | International Solidarity Movement, Nablus Team | Burin, Occupied Palestine Tuesday afternoon, the 7th of October, olive farmer Mahmoud Rga Mahoud Aid, his wife, and thei three children were attacked by a a group of settlers from the illegal settlement of Giv’at Ya’akov. The attack took place on the family´s land near the village of Burin, south…